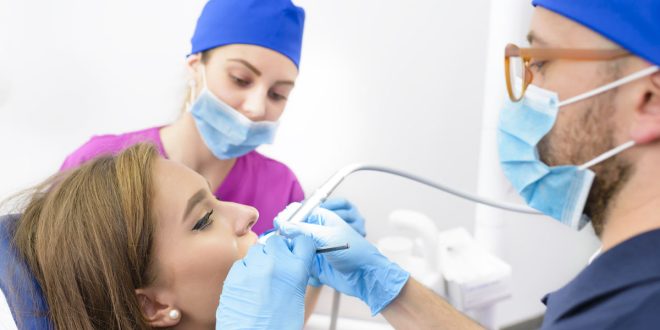
An oral surgeon is a dental specialist who has received advanced training and education in the diagnosis and surgical treatment of conditions affecting the mouth, teeth, jaws, and facial structures. They are also known as maxillofacial surgeons or oral and maxillofacial surgeons.
Some of the procedures that an oral surgeon may perform include wisdom teeth extractions, dental implant surgery, jaw surgery, bone grafting, and treatment of oral cancer. They may also provide cosmetic procedures such as facelifts, rhinoplasty, and chin augmentation.
Oral surgeons often work closely with other dental specialists, such as orthodontists and periodontists, to provide comprehensive care to patients with complex dental and facial issues.
To become an oral surgeon, one must complete dental school and then complete an additional four to six years of specialized training in oral and maxillofacial surgery. This includes both clinical and surgical training, as well as the completion of a residency program. Oral surgeons must also obtain a license to practice in their state and may choose to become certified by the American Board of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.
What Does An Oral Surgeon Do?
An oral surgeon is a dental specialist who performs surgical procedures related to the mouth, jaw, and face. Oral surgeons are also known as maxillofacial surgeons.
Oral surgeon dentists typically perform procedures such as tooth extractions, dental implant placement, corrective jaw surgery, cleft palate or lip repair, and the removal of tumors and cysts in the mouth and face. They may also treat facial trauma and injuries to the teeth and jaws.
Oral surgeons have extensive training and education beyond dental school, including completing a four- to a six-year residency program in oral and maxillofacial surgery. They may also have a medical degree in addition to their dental degree.
Oral surgeons work closely with other dental specialists, such as orthodontists and periodontists, as well as medical professionals such as anesthesiologists and plastic surgeons, to provide comprehensive care for their patients.
What Is The Difference Between Oral And Dental Surgeons?
An oral surgeon is a specialist who is trained to perform surgical procedures on the mouth, teeth, gums, and jaw. They typically complete four to six years of additional training after dental school and are skilled in a variety of surgical procedures, including tooth extraction, dental implants, and jaw reconstruction.
A dental surgeon, on the other hand, is a general dentist who has received additional training in surgical procedures related to teeth and gums. They can perform minor surgeries, such as tooth extractions and gum surgeries, but they are not trained to perform more complex procedures like jaw reconstruction or dental implants.
In summary, while both oral and dental surgeons have advanced training in performing surgical procedures, oral surgeons have a more specialized focus on complex procedures involving the jaw and facial structures, while dental surgeons perform more routine surgical procedures related to the teeth and gums.
Oral Surgeon Services
An oral surgeon is a dental specialist who focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of conditions related to the mouth, jaw, and facial regions. They perform a variety of surgical procedures, ranging from routine tooth extractions to more complex surgeries such as dental implants, jaw surgery, and reconstruction following trauma or disease.
Some of the services that an oral surgeon dentist may offer include:
Tooth Extractions:
Oral surgeons are trained to perform all types of tooth extractions, including impacted wisdom teeth, damaged teeth, and teeth that need to be removed for orthodontic treatment.
Dental Implants:
Oral surgeon dentists are trained to place dental implants, which are artificial tooth roots that support dental prosthetics such as crowns, bridges, and dentures.
Jaw Surgery:
Oral surgeons can perform corrective jaw surgery to improve the alignment of the jaw, correct bite issues, and alleviate pain and discomfort.
Facial Trauma Reconstruction:
Dental and Oral surgeons can reconstruct facial bones and tissues that have been damaged due to trauma, such as fractures and lacerations.
Oral Pathology:
Oral surgeons can diagnose and treat conditions such as oral cancer, cysts, and tumors.
TMJ Disorders:
Oral surgeons can diagnose and treat temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, which can cause pain and discomfort in the jaw joint and surrounding muscles.
If you are in need of any of these services, it is important to consult with an experienced and qualified oral surgeon who can evaluate your specific needs and provide the appropriate treatment.
What Happens During Oral Surgery?
Oral surgery is a type of surgery that involves the treatment of conditions affecting the mouth, teeth, jaws, and other related structures. The procedures performed during oral surgery can vary widely depending on the specific condition being treated.
Some common procedures include:
Tooth Extraction:
The removal of a tooth or teeth that damaged, decayed, or causing pain or other problems.
Dental Implant Surgery:
The placement of an artificial tooth root into the jawbone to support a replacement tooth or bridge.
Jaw Surgery:
The repositioning of the jawbone to correct misalignment or to treat conditions such as temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders.
Biopsy:
The removal of a small piece of tissue for examination to determine whether it is cancerous or not.
Treatment Of Facial Injuries:
Repair of facial injuries caused by trauma, such as a broken jaw or a laceration to the mouth or face.
During oral surgery, local anesthesia typically used to numb the area treated, and in some cases, general anesthesia may used to keep the patient sedated and comfortable throughout the procedure.
Once the anesthesia has taken effect, the surgeon will make incisions as needed and perform the necessary procedures. After the surgery is complete, the patient will monitored for a period of time to ensure that there are no complications, and medication may prescribed to manage pain and reduce swelling.
What Are The Advantages Of Oral Surgery?
Oral surgery can provide several advantages, including:
Relieving Pain:
Oral surgery can help to alleviate pain associated with various dental problems such as impacted wisdom teeth, abscesses, and temporomandibular joint disorders (TMJ).
Improving Function:
Oral surgery can improve the function of your teeth and jaw, allowing you to eat and speak more comfortably and effectively.
Correcting Facial Deformities:
Oral surgery can used to correct facial deformities such as cleft lip and palate and jaw misalignments.
Improving Oral Health:
Oral surgery can help to remove diseased or damaged teeth, reducing the risk of further dental problems.
Enhancing Appearance:
Oral surgery can help to improve the appearance of your smile by correcting issues such as missing teeth, uneven gum lines, and misaligned jaws.
Faster Recovery:
Oral surgery techniques have improved greatly over the years, resulting in faster and less painful recovery times.
Preventing Future Problems:
Oral surgery can prevent future dental problems by addressing underlying issues and ensuring proper alignment of the teeth and jaw.
What Are The Risks Or Complications Of Oral Surgery?
Oral surgery refers to any type of surgical procedure performed in the mouth or jaw area, such as tooth extraction, dental implants, jaw surgery, or gum surgery. Like any surgical procedure, oral surgery carries some risks and potential complications.
Some of the common risks and complications associated with oral surgery include:
Bleeding:
Bleeding is a common complication after any type of oral surgery. However, excessive bleeding can be a serious problem, and patients may need to have additional procedures or medication to control it.
Infection:
Infection is another common complication that can occur after oral surgery. It can cause pain, swelling, fever, and other symptoms. Antibiotics may required to treat the infection.
Nerve Damage:
Nerve damage can occur during oral surgery, especially if the procedure involves the jaw or wisdom teeth. This can result in numbness or tingling in the mouth, lips, or tongue, and may be temporary or permanent.
 Posting Point
Posting Point