How to Deal with IBS
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a gastrointestinal disorder. It affects both the small and large intestines. With IBS, your gut becomes more sensitive. And its muscular contractions don’t work the way they should.
IBS is considered a functional disorder. As there is nothing wrong with the actual structure of your bowel — the problem is with how it works. People with IBS usually experience multiple symptoms that include:
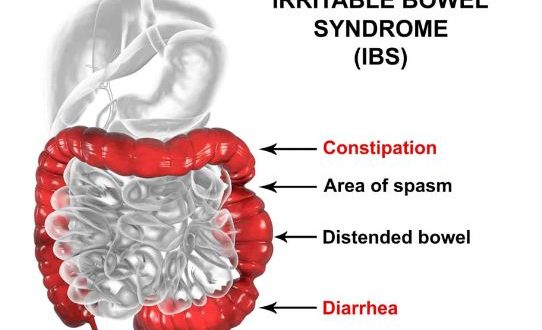
- Abnormalities in bowel movement with abdominal pain and cramping.
- Constipation that generally appears with incomplete bowel movement
- Diarrhea with an urgent need to move the bowels
- Gas and bloating
- Urge to move the intestines, but an inability to do so
- Mucus in the stool
Diet and cold can induce symptoms of aggravated or recurring IBS. Many of us don’t know that irritable bowel syndrome comes in several different forms. And different kinds of IBS have different treatments. Taking medication blindly often leads to irritable bowel syndrome or long-term/chronic problems. Making it difficult to cure IBS in a better way.
Subtypes of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
IBS has three subtypes, and they are equally common:
- Alternating type IBS (IBS-A)
- It deals with diarrhea and constipation. People with IBS-A suffer from both conditions from time to time.
- Diarrhea-predominant IBS (IBS-D)
- This condition appears with regular bowel movements. Constant feelings of urgency, and loose and watery stools. It is commonly called IBS-D.
- Constipation-predominant IBS (IBS-C)
- IBS-C is about infrequent bowel movements, stomach pain, bloating, hard or lumpy stools, discomfort, and straining during bowel movements.
How to deal with IBS?
To deal with IBS, your eating habits matter most. What we eat and what we don’t both impact IBS symptoms significantly. Initially. It is essential to stop eating foods associated with IBS symptoms.
These foods include fatty food. Dairy products, chocolate, alcohol, caffeine and fried items. Also, it is good to consider avoiding soft drinks. Sports drinks and fruit juices.
A second important step is doing anything to manage your stress levels. Managing stress can help to control the emotional response to IBS. Stress not only can trigger symptoms, but it can often make them long-lasting or even worse. People also use fiber supplements or laxatives to deal with constipation. Using loperamide is also common to help with diarrhea.
Can probiotics make a difference?
The best possible option to deal with IBS is the regular use of probiotic food and supplements. Probiotics are live microbes that are consumed from fermented food and dairy items such as yogurt. Cheese. Probiotics are excellent for helping with intestinal problems. These supplements restore bacterial balance in the gut and enhance the immune system.
Probiotics deal with the issue:
Probiotics resolve leading causes of IBS by:
- Inhibiting the growth and population of disease-causing bacteria
- Enhancing the barrier functions of the immune system
- Fighting against inflammation
- Slowing down bowel movements
- Balancing the gut flora to decrease gas production
- Reducing the gut’s sensitivity to gas buildup
Probioform
Probioform is an extremely effective living-liquid probiotic that both aids in digestion and regulates bowel movements. Proform ensures regular bowel movements by promoting the effective absorption. Assimilation of food. It also drastically reduces the potential for disease and provides increased energy to make you healthy.
Read More: How Long Does it Take to Get Results for a Coronavirus Disease Test?
 Posting Point
Posting Point